Plastic injection molding manufacturing stands as a linchpin in the world of industrial production, playing a pivotal role in shaping the products that populate our daily lives. This sophisticated process, marked by precision and efficiency, has become the cornerstone of various industries, providing a scalable and reliable method for crafting intricate plastic components.
The Anatomy of Plastic Injection Molding
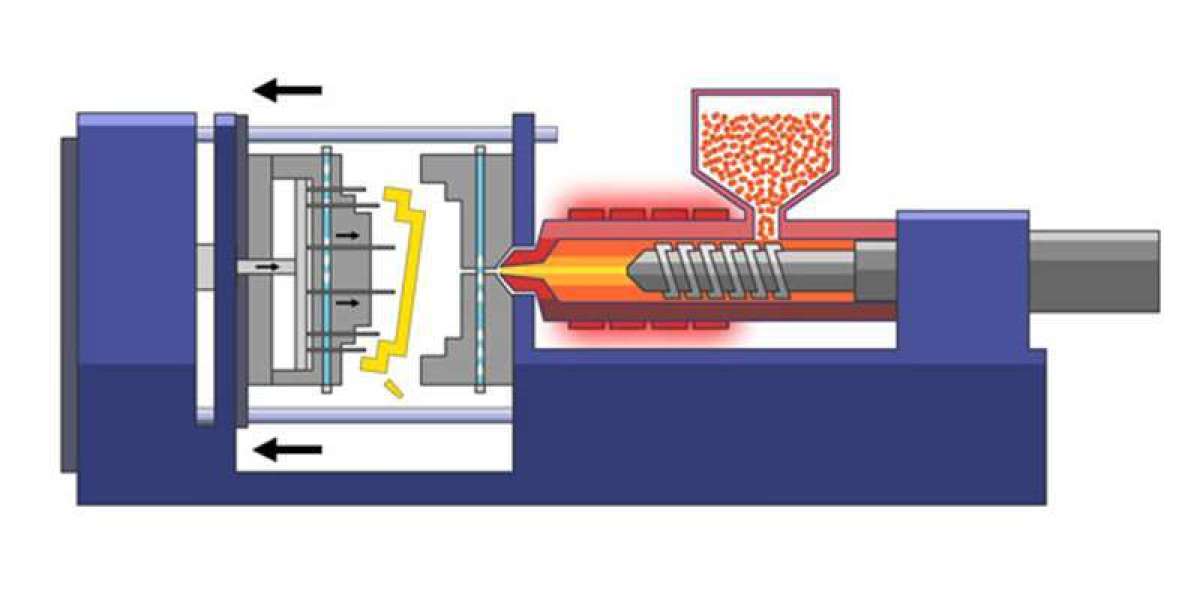
1. Crafting the Blueprint: Molds and Tooling
At the heart of plastic injection molding is the creation of molds, often machined from durable materials like aluminum or steel. These molds serve as the blueprints for the final product, dictating its form and intricacies. The process starts with the careful design and engineering of these molds, a crucial step that sets the stage for the entire manufacturing journey.
2. Material Transformation: From Pellets to Molten Gold
The chosen plastic material, typically in the form of small pellets, undergoes a transformative journey in the plastic injection molding process. These pellets are fed into a heated barrel, where they are subjected to controlled temperatures and pressures. A helical-shaped screw within the barrel ensures thorough mixing, transforming the pellets into a molten state ready for molding.
3. Precision Injection: Filling the Mold Cavity
Once the molten plastic reaches the desired state, it is injected into the meticulously crafted mold. The injection is a precise process, ensuring that the molten material fills every nook and cranny of the mold cavity. This stage demands a delicate dance of timing and pressure to guarantee the accurate replication of the mold's design.
4. Cooling and Solidification: Shaping the Final Form
As the molten plastic enters the mold, the cooling process begins. Cooling lines, strategically placed, aid in expediting this phase. The molten material solidifies, adopting the exact shape and features of the mold. The cooling time is a critical parameter, influencing the overall efficiency of the process.
5. Ejection and Inspection: Bringing the Product to Light
Once solidified, the newly formed plastic component is ready for extraction. The mold opens, and ejector pins facilitate the removal of the part. This is followed by a meticulous inspection to ensure that the product meets the stringent quality standards. Defects, if any, are identified and addressed to maintain the precision that defines plastic injection molding.
Scalability and Efficiency: The Advantages of Injection Molding
1. Mass Production Mastery
One of the primary advantages of plastic injection molding is its ability to facilitate mass production with unparalleled efficiency. The process allows for the creation of thousands or even millions of identical parts, ensuring consistency in every unit. This scalability is a key driver for the widespread adoption of injection molding in various industries.
2. Cost-Effectiveness Unleashed
While the initial costs, particularly for tooling, can be substantial, the per-unit cost diminishes significantly as production scales up. Once the molds are created, subsequent units can be manufactured at a relatively low cost. The cost-effectiveness of injection molding becomes especially pronounced when compared to other manufacturing processes, such as CNC machining.
3. Minimal Material Wastage
Unlike traditional manufacturing methods that involve cutting away excess material, injection molding produces minimal wastage. The only waste generated typically comes from the sprue, runners, gate locations, and any overflow material (commonly known as 'flash'). This reduction in material wastage aligns with modern sustainability goals.
4. Consistency in Replication
The precision inherent in injection molding ensures that each part is an exact replica of the others. This consistency is crucial, particularly in industries where identical components are a necessity. It also enhances the reliability of the final product, contributing to its overall quality.
Challenges and Considerations in Plastic Injection Molding Manufacturing
1. Upfront Investment Complexity
One of the notable challenges in plastic molding manufacturing is the upfront investment required. The creation of molds and tooling demands a significant financial commitment. This can be a barrier for smaller businesses or startups looking to enter the realm of injection molding.
2. Size Limitations and Design Complexity
While injection molding excels in producing small to medium-sized parts with intricate details, it faces challenges with larger components. Size limitations of injection molding machines and the physical constraints of molds can necessitate the creation of larger parts as multiple pieces, adding complexity to the assembly process.
3. Experienced Design for Undercuts
The presence of undercuts, recessed areas that make part ejection challenging, requires experienced design considerations. Addressing undercuts effectively without compromising the structural integrity of the part demands a level of expertise in mold design.
Evolution of Materials in Plastic Injection Molding
1. The Reign of Thermoplastics and Thermosets
Traditionally, thermoplastics and thermosetting polymers have been the stalwarts in plastic injection molding. Their versatility, ease of processing, and ability to undergo repeated heating and cooling cycles make them ideal for this manufacturing process.
2. Diversification with Advanced Polymers
In recent years, the landscape has witnessed the integration of advanced polymers into the injection molding arena. Materials such as Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK), Polyphenylsulfone (PPSU), and Polyetherimide (PEI) bring heightened temperature resistance, flame retardancy, and enhanced chemical resistance to the table. This diversification broadens the application spectrum of plastic injection molding.
3. Sustainability in Focus
As environmental concerns take center stage, there's a growing emphasis on using materials that align with sustainability goals. The injection molding industry is witnessing a shift towards materials with eco-friendly attributes, contributing to a more responsible approach to manufacturing.
Future Horizons: Technological Advancements
1. Smart Manufacturing Integration
The advent of Industry 4.0 is making its presence felt in the realm of plastic injection molding. Smart manufacturing practices, involving the integration of sensors, data analytics, and automation, are optimizing the efficiency of injection molding processes. Real-time monitoring and control mechanisms contribute to enhanced quality and reduced downtimes.
2. Enhanced Energy Efficiency
Modern injection molding machinery is evolving to be more energy-efficient. Compared to a decade ago, contemporary machines consume between 20 and 50% less energy. This not only aligns with sustainability goals but also contributes to cost savings in the long run.
3. Innovations in Tooling Technology
Advancements in tooling technology are driving efficiency and precision in injection molding. From multi-cavity molds to innovative cooling strategies, these innovations are reshaping the landscape of plastic injection molding manufacturing, making it more versatile and adaptable to evolving demands.
Conclusion: Precision, Efficiency, and Beyond
In the intricate dance of molten plastic, precision tooling, and manufacturing prowess, plastic injection molding manufacturing emerges as a titan in the world of industrial production. Its ability to deliver consistent, high-quality components at scale has solidified its place in various industries, from automotive to consumer goods.
As we look toward the future, the trajectory of plastic injection molding is marked by a commitment to sustainability, technological innovation, and a continuous quest for efficiency. With each injection, the industry molds not just plastics but the very fabric of modern manufacturing, shaping a future where precision and efficiency coalesce in the creation of tomorrow's products.