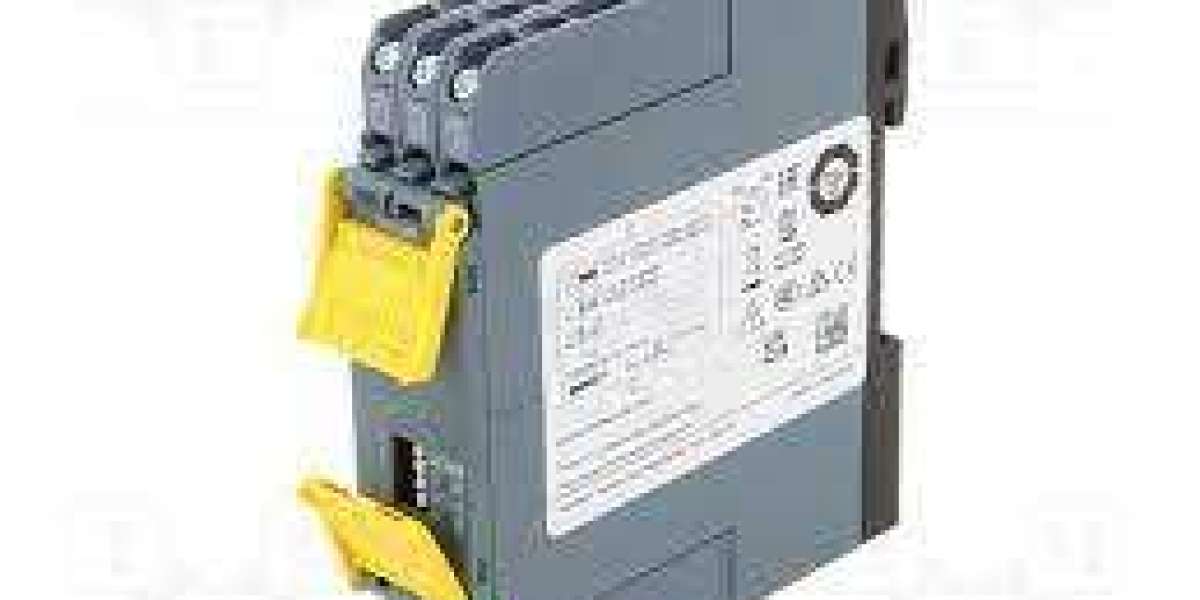
These precision devices play a pivotal role in controlling electrical circuits, ensuring safety, efficiency, and reliability. Whether you are designing a new electrical system or replacing relays in an existing setup, understanding and addressing environmental considerations is paramount to achieving optimal performance and longevity. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the critical environmental factors that impact Siemens relay installations.
- Temperature Extremes:
Temperature is a fundamental environmental factor that profoundly affects Siemens relay performance. Relays have specified operating temperature ranges, and operating outside these ranges can result in malfunctions or permanent damage.
High Temperatures: In environments with high temperatures, relays can overheat, causing insulation breakdown and degradation of internal components. Proper ventilation, heat sinks, or cooling systems should be employed to maintain safe operating temperatures.
Low Temperatures: Cold temperatures can cause relay contacts to become less responsive, potentially leading to slow or unreliable switching. In extremely low temperatures, condensation may form, increasing the risk of short circuits. Insulation and heating solutions are essential in cold environments.
- Humidity and Moisture:
Moisture and humidity are common environmental challenges in many applications. Excessive moisture can lead to corrosion, electrical leakage, and insulation breakdown.
Protection from Moisture: Siemens relays should be housed in enclosures that provide protection against moisture and humidity. Sealed enclosures with appropriate IP (Ingress Protection) ratings are essential, along with gaskets and seals to maintain a dry interior.
Condensation Control: Implementing dehumidifiers or heaters within the enclosure can prevent condensation, even in humid environments. Adequate drainage systems should also be in place to remove any accumulated water.
- Dust and Contaminants:
Industrial settings often expose relays to dust, dirt, and airborne contaminants. Accumulation of these particles can lead to decreased performance and even failure.
Air Filtration: Use air filters or filter vents in the enclosure to prevent dust and contaminants from entering and settling on relay components. Regular maintenance should include cleaning relay components to ensure their longevity.
- Corrosive Substances:
In environments where corrosive substances are present, such as chemicals or saltwater, special considerations are necessary to prevent corrosion and damage to relay components.
Corrosion-Resistant Materials: Select relay models constructed with materials that resist corrosion. Stainless steel enclosures and coatings can be effective in protecting against corrosive substances.
- Vibration and Shock:
Applications with significant mechanical vibrations or shocks require proper mounting and dampening solutions to prevent relay malfunctions or physical damage.
Shock Absorption: Mount relays securely using shock-absorbing techniques to minimize the impact of vibrations and shocks.
- UV Exposure:
Relays installed outdoors may be exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. Prolonged UV exposure can lead to material degradation and affect relay performance.
UV-Resistant Enclosures: Utilize enclosures designed to resist UV radiation or provide shading to protect relays from direct sunlight.
- Altitude:
Altitude can impact relay performance, particularly in high-altitude locations where air pressure is lower. Lower air pressure affects the relay's ability to dissipate heat.
Derating: At higher altitudes, relay derating may be necessary. This involves selecting relays with higher current ratings to compensate for reduced heat dissipation efficiency due to lower air pressure.
- Compliance with Environmental Regulations:Ensure that your relay installations adhere to local and international environmental regulations and standards, especially when dealing with hazardous substances or specific industrial applications.
Conclusion:
Siemens relays are critical components in electrical systems, and their proper functioning is essential for the reliability and safety of various applications. Environmental considerations should be at the forefront of any relay installation project. Understanding and addressing factors such as temperature extremes, humidity, moisture, dust, contaminants, corrosive substances, vibration, shock, UV exposure, altitude, and compliance with environmental regulations are key to ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of Siemens relays. By meticulously accounting for these environmental factors, you can trust that your relay installations will meet the demands of diverse operating conditions and contribute to the efficiency and reliability of your electrical systems.
The Evolution of Protective Relays: From Mechanical to Digital
The Power of Precision Exploring Numerical Relays in Electrical Systems