Title: Understanding the Complexities of High Blood Pressure: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract:
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a pervasive cardiovascular condition that poses a significant global health challenge. This paper provides a comprehensive review of high blood pressure, encompassing its epidemiology, etiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, management, and preventive strategies. The paper emphasizes the importance of a multidisciplinary approach in addressing this public health concern and explores the latest research developments and therapeutic interventions aimed at controlling high blood pressure.
Keywords: High blood pressure, Hypertension, Cardiovascular disease, Epidemiology, Etiology, Risk factors, Pathophysiology, Clinical manifestations, Diagnosis, Management, Prevention, Multidisciplinary approach, Therapeutic interventions, Public health.
1. Introduction
High blood pressure, often referred to as hypertension, is a widespread and critical health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a leading cause of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes, making it a major contributor to global morbidity and mortality. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive review of high blood pressure, highlighting its various facets and addressing the current state of knowledge in epidemiology, etiology, risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, management, and preventive strategies.
2. Epidemiology
High blood pressure is a global health problem that affects people of all ages, genders, and ethnicities. It is estimated that approximately 1.13 billion individuals worldwide suffer from hypertension, with a rising prevalence in both developed and developing countries. Understanding the epidemiological trends and patterns of hypertension is crucial for effective public health planning and resource allocation.
3. Etiology
The etiology of high blood pressure is multifactorial and involves genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. This section delves into the underlying causes of hypertension, including genetic predisposition, excessive salt intake, obesity, and stress. The interplay of these factors contributes to the development and progression of the condition.
4. Risk Factors
Identifying risk factors associated with high blood pressure is essential for early detection and intervention. This section discusses modifiable risk factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, diet, physical inactivity, and non-modifiable risk factors like age, gender, and family history. It also explores the role of comorbidities such as diabetes and chronic kidney disease in exacerbating hypertension.
5. Pathophysiology
Understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms behind high blood pressure is critical for developing targeted therapeutic interventions. This section elucidates the intricate processes involving the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, sympathetic nervous system, endothelial dysfunction, and oxidative stress. It highlights the interactions among these systems and their contribution to elevated blood pressure.
6. Clinical Manifestations
Hypertension often remains asymptomatic for an extended period, earning its moniker as the "silent killer." This section explores the clinical manifestations that may occur when hypertension is left untreated, including headaches, visual disturbances, fatigue, and organ damage to the heart, brain, kidneys, and blood vessels. Early recognition of these signs is vital for timely intervention.
7. Diagnosis
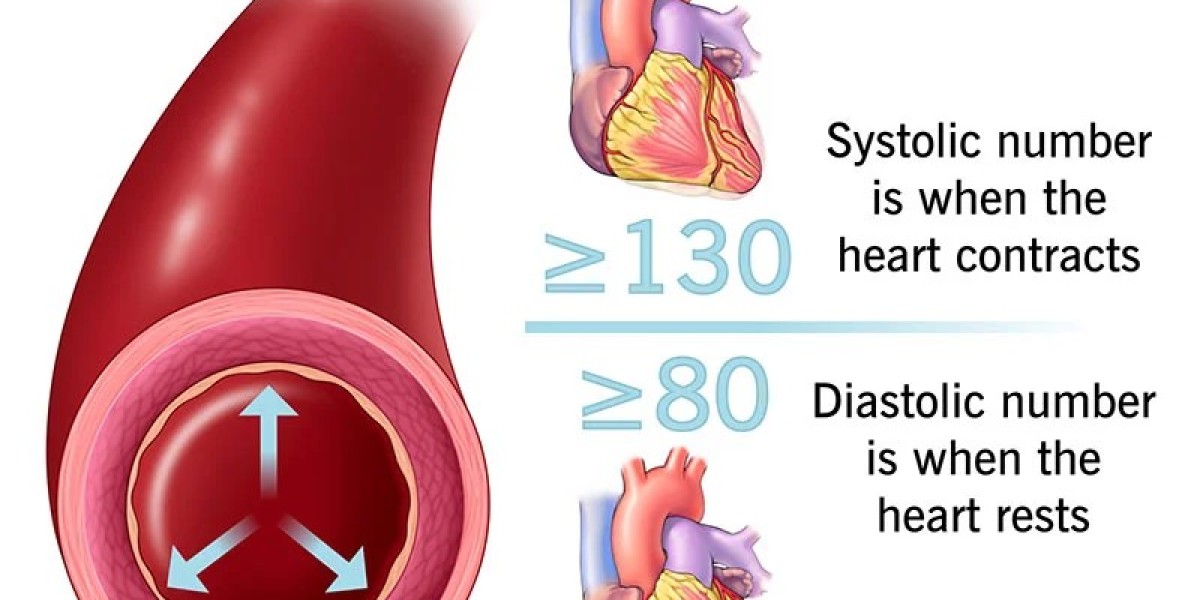
Accurate diagnosis of hypertension is essential for effective management. This section outlines the diagnostic criteria and techniques, including blood pressure measurement, ambulatory monitoring, and home blood pressure monitoring. It also discusses the importance of multiple readings and the white coat effect in achieving an accurate diagnosis.
8. Management
Managing high blood pressure involves a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle modifications, pharmacological therapies, and patient education. This section explores the dietary strategies, physical activity recommendations, and medications used in hypertension management. It also emphasizes the importance of patient compliance and adherence to treatment plans.
9. Prevention
Preventing hypertension and its complications is a key public health goal. This section discusses primary prevention strategies, including health promotion campaigns, policy initiatives to reduce salt intake, and smoking cessation programs. It also underscores the importance of secondary prevention through early detection and management of high blood pressure.
10. Multidisciplinary Approach
The management of hypertension necessitates a multidisciplinary approach involving healthcare professionals, researchers, policymakers, and the community. This section underscores the importance of collaboration in raising awareness, conducting research, and implementing effective interventions to combat hypertension on a global scale.
11. Therapeutic Interventions
Advancements in therapeutic interventions for hypertension are continuously evolving. This section discusses emerging treatments such as novel antihypertensive drugs, precision medicine, and digital health technologies. It highlights ongoing research efforts aimed at improving the management of high blood pressure.
12. Conclusion
High blood pressure remains a significant global health challenge, affecting a substantial portion of the population and contributing to a myriad of cardiovascular diseases. This comprehensive review has covered various aspects of hypertension, from its epidemiology and etiology to risk factors, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, management, and prevention. A multidisciplinary approach, coupled with ongoing research and innovation, is essential to address this public health concern effectively and reduce its burden on society.
Keywords: High blood pressure, Hypertension, Cardiovascular disease, Epidemiology, Etiology, Risk factors, Pathophysiology, Clinical manifestations, Diagnosis, Management, Prevention, Multidisciplinary approach, Therapeutic interventions, Public health.