The energy market, a colossal and intricate web that powers our modern world, is on the cusp of a seismic transformation. The agent of this change? Artificial Intelligence. Far from being a futuristic fantasy, AI is already weaving its intricate algorithms into the very fabric of how one even thinks about energy. AI in energy market is revolutionizing the way energy is produced, transmitted, distributed, and consumed, enabling a more efficient, sustainable, and reliable energy system. Let us explore AI's electrifying role in the energy landscape – a journey from power plant to smart plug, and beyond.
The Spark of Genius: AI's Current Power Plays in the Energy Arena
Today, AI is not just a buzzword in the energy sector; it's a workhorse, performing a multitude of tasks that were previously challenging, inefficient, or simply impossible. For instance, on September 6, 2024, Schneider Electric launched an AI-powered feature for its Wiser Home app. This feature optimizes home energy management by automating and predicting energy consumption for water heaters and EV chargers.
- Predictive Prowess – Forecasting Demand and Supply: AI forecasts energy demand and supply by analyzing data, enabling utilities to optimize generation, minimize waste, and prevent shortages. It also forecasts renewable energy output for better grid integration. China's Suola wind farm uses AI to boost efficiency and reduce costs.
- Grid Modernization – The Rise of the Smart Grid: The traditional power grid is getting an IQ boost, thanks to AI. Smart grids utilize AI for real-time monitoring, analysis, and control of energy flows. This means:
- Optimized Distribution: AI algorithms dynamically adjust energy distribution, minimizing transmission losses and ensuring power reaches where needed most efficiently.
- Fault Detection and Predictive Maintenance: AI predicts equipment failures (transformers, power lines, substations) using sensor data, thermal imaging, and acoustics, enabling proactive maintenance, reducing downtime, and improving grid reliability.
- Enhanced Resilience: AI helps grids respond faster and more effectively to disruptions, whether from extreme weather events or cyber threats. It can reroute power, isolate faults, and rapidly restore services.
- Renewable Revolution – Making Green Energy Smarter: The Achilles' heel of renewables, intermittency, is being tackled head-on by AI.
- Improved Forecasting: AI models analyze weather patterns, satellite imagery, and historical performance data to provide highly accurate solar and wind generation forecasts.
- Optimized Integration: AI helps balance the variable output of renewables with the stable demand of the grid, managing energy storage systems (like batteries) to store excess renewable energy and release it when demand is high or renewable generation is low.
- Efficient Operations: AI optimizes the performance of renewable energy assets, such as adjusting the tilt of solar panels or the pitch of wind turbine blades for maximum energy capture.
- Energy Efficiency – Less is More: AI is a powerful tool for optimizing energy consumption across various sectors:
- Smart Buildings: AI-powered building management systems learn occupancy patterns and environmental conditions to optimize heating, cooling, and lighting, significantly reducing energy waste in commercial and residential buildings.
- Industrial Optimization: In manufacturing, AI analyzes processes to identify energy inefficiencies and suggests improvements, leading to substantial cost savings and a smaller carbon footprint.
- Personalized Energy Management: AI can provide consumers real-time insights and recommendations for reducing energy usage. Projects like CSIRO's RapidRate in Australia use AI to estimate home energy efficiency.
- Trading and Market Dynamics: AI algorithms are increasingly used in energy trading. They analyze market trends, predict price fluctuations, and execute trades at lightning speed to optimize procurement strategies and hedge against price volatility.
- EV Infrastructure Optimization: AI optimizes EV charging infrastructure placement and manages charging schedules to prevent grid overload and cut costs as EVs become mainstream. Reinforcement learning models can adjust charging station pricing in real-time based on grid congestion.
- Exploration and Production: In the oil and gas sector, AI analyzes geological data to identify potential reserves and optimize drilling operations, enhancing safety and efficiency.
Navigating the Double-Edged Sword: AI's Own Energy Appetite
Balancing AI's benefits with its energy footprint is a key challenge, but the industry is pursuing solutions.
- Hardware Innovations: The development of more energy-efficient chips (like IBM's Telum II Processor) and power-capping hardware has come like a breath of fresh air.
- Smarter AI Models: Stakeholders are contemplating the creation of smaller, more specialized AI models that require less energy than generalist large language models for specific tasks.
- Efficient Training Techniques: Optimizing the model training process to reduce redundant computations and energy use may augur well.
- Renewable-Powered AI: Smart planning, such as locating data centers in regions with abundant renewable energy and sourcing green energy, can negate AI’s energy cost.
- Open Source Collaboration: Companies can gain from sharing best practices and tools to build more energy-efficient AI systems.
Peering into the Crystal Ball: The Future of AI in Energy
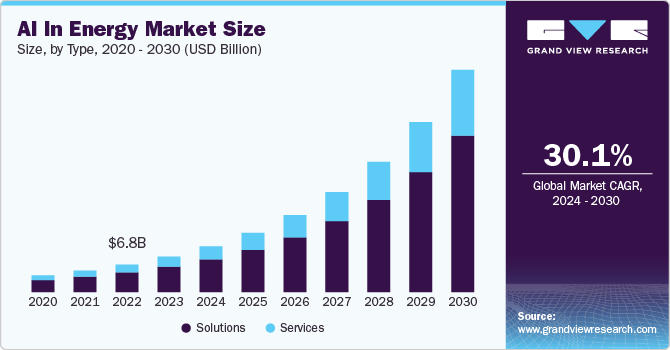
The AI in energy market is booming, projected to grow from USD 8.75 billion in 2024 to an astounding USD 54.82 billion by 2030. This explosive growth hints at an even more integrated and transformative future:
- Autonomous Energy Systems: Imagine self-healing grids and fully automated power plants managed by AI, capable of making complex decisions in real-time to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and security.
- Hyper-Personalized Energy Solutions: AI could offer highly customized energy plans and advice to individual consumers and businesses, optimizing their energy use down to the appliance level.
- AI-Driven Materials Discovery: Generative AI is already being explored to design and optimize low-carbon materials, such as new types of cement, which currently account for a significant portion of global carbon emissions.
- Quantum AI for Unsolvable Problems: Quantum computing, combined with AI, could tackle highly complex optimization problems in energy distribution, resource allocation, and grid management that are currently beyond the reach of classical computers.
- Enhanced Carbon Capture and Storage (CCUS): AI can optimize the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of CCUS technologies, crucial for mitigating emissions from hard-to-abate industries.
- Decentralized Energy Networks: AI will be key in managing smaller, interconnected microgrids and distributed energy resources (like rooftop solar and local battery storage), reducing reliance on large, centralized utilities and increasing energy resilience.
- Dynamic Pricing and Real-Time Markets: AI will enable more sophisticated dynamic pricing models that adapt instantly to supply and demand, encouraging consumers to shift their energy use to off-peak hours.
Navigating the Challenges: Roadblocks on the AI-Energy Superhighway
Despite the immense promise, the path to a fully AI-integrated energy future is not without its hurdles:
- Data Dilemmas: AI thrives on data. The energy sector needs to address challenges related to data quality, accessibility, standardization, and centralization.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Many existing energy infrastructures are antiquated, making integration with modern AI systems complex and costly.
- Cybersecurity Imperative: Cyberattack risks increase as AI becomes more embedded in critical energy infrastructure. Robust cybersecurity measures are paramount.
- Regulatory Landscapes: Policymakers and regulators need to adapt and create frameworks that foster innovation while ensuring safety, privacy, and ethical AI deployment.
- High Implementation Costs: The upfront investment in AI technologies, infrastructure, and skilled personnel can be substantial.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Handling vast amounts of energy consumption data raises legitimate privacy concerns that must be addressed through strong data governance and anonymization techniques.
The Power of Tomorrow, Programmed Today
AI is a fundamental shift for the energy sector, promising a more efficient, reliable, sustainable, and resilient ecosystem. Despite the challenge of AI's energy use, its overall trajectory points to it being an indispensable tool for a cleaner energy future. From optimizing wind turbines to ensuring grid reliability, AI is increasingly shaping our energy world, making its future brighter and smarter.



