Introduction:
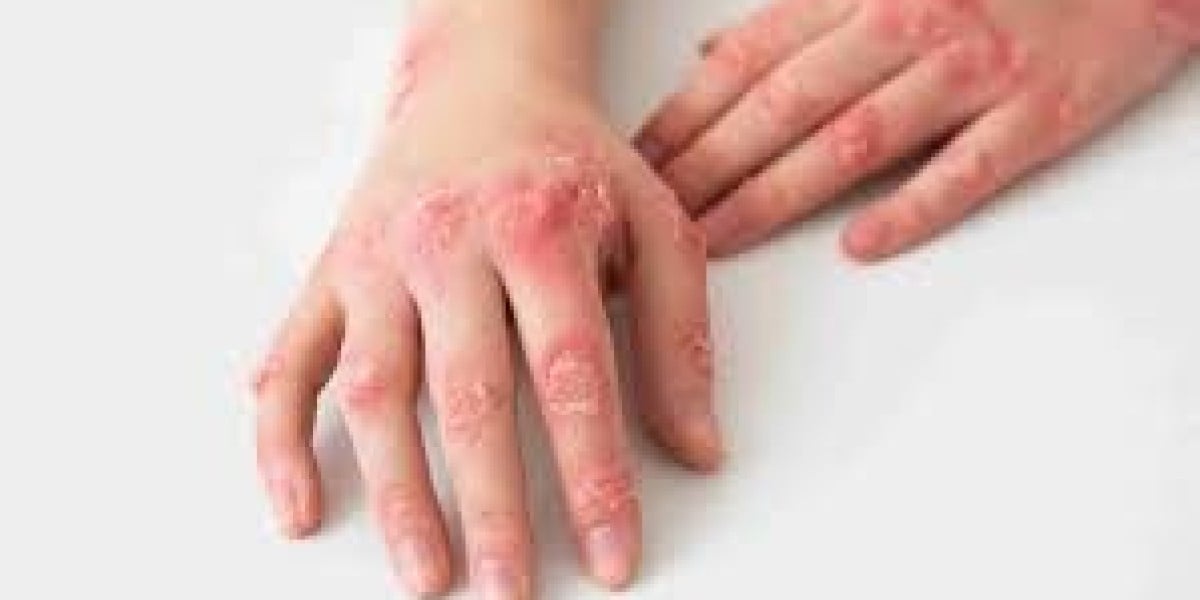
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. While the exact cause of eczema is not fully understood, research has increasingly shown a connection between the gut and the development of eczema. This article explores the relationship between eczema and the gut, highlighting the role of the gut microbiome and discussing treatment approaches that target the gut to manage eczema symptoms. Eczema treatment in Abu Dhabi can help.
The Gut Microbiome and Eczema:
The gut microbiome refers to the trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, that reside in our digestive tract. These microorganisms play a crucial role in maintaining the health and balance of our immune system. Recent studies have indicated that alterations in the composition and diversity of the gut microbiome can contribute to the development of eczema.
Research has found that individuals with eczema often have an imbalance in their gut microbiota, characterized by a lower diversity of beneficial bacteria and an overgrowth of harmful bacteria. This imbalance can lead to a weakened immune response and increased inflammation, which can trigger or exacerbate eczema symptoms.
The Gut-Brain-Skin Axis:
The gut microbiome is connected to the skin through what is known as the gut-brain-skin axis. This axis represents the communication between the gut, the central nervous system, and the skin. Disruptions in this axis can contribute to the development of various skin conditions, including eczema.
When the gut microbiome is imbalanced, it can lead to increased intestinal permeability, commonly referred to as "leaky gut." This allows toxins and inflammatory molecules to escape from the gut into the bloodstream, triggering an immune response and inflammation throughout the body. This inflammation can manifest on the skin as eczema flare-ups.
Treatment Approaches:
Understanding the connection between eczema and the gut has opened up new possibilities for treatment approaches that target the gut microbiome. Here are some strategies that have shown promise in managing eczema symptoms:
1. Probiotics: Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can be consumed through certain foods or supplements. Studies have found that specific strains of probiotics, such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Bifidobacterium lactis, can help improve eczema symptoms by restoring the balance of gut bacteria and strengthening the immune response.
2. Prebiotics: Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. Consuming prebiotic-rich foods like onions, garlic, bananas, and oats can support a healthy gut microbiome and potentially reduce eczema symptoms.
3. Dietary Modifications: Some individuals with eczema may benefit from identifying and avoiding trigger foods that can worsen symptoms. Common triggers include dairy, gluten, eggs, and certain fruits or vegetables. Working with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian can help develop a personalized elimination diet plan.
4. Gut-Healing Supplements: Certain supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and zinc, have been found to support gut health and reduce inflammation. These supplements can complement other treatment approaches but should be taken under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Conclusion:
Recognizing the connection between eczema and the gut provides valuable insights into potential treatment approaches for managing this chronic skin condition. By focusing on restoring gut health through probiotics, prebiotics, dietary modifications, and gut-healing supplements, individuals with eczema may experience relief from symptoms and achieve better overall well-being. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a personalized approach to managing eczema based on individual needs and considerations.