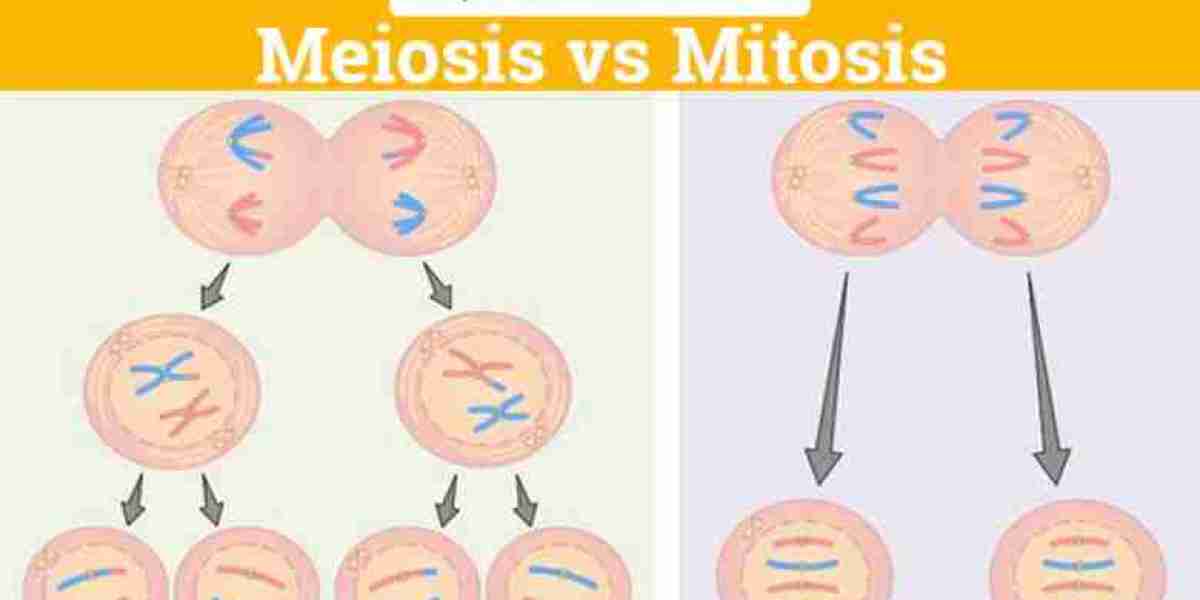
While both involve the division of cells, they serve distinct purposes and occur under different circumstances. Understanding the differences between mitosis and meiosis is crucial for grasping the complexities of cellular biology. Let's explore these processes in detail and unravel the mysteries with homework help assistance.
Mitosis: Cell Division for Growth and Repair
Mitosis is a process of cell division that occurs in somatic cells—cells that make up the body tissues—and is primarily responsible for growth, repair, and maintenance. It consists of several distinct stages, including prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, each characterized by specific events such as chromosome condensation, alignment, separation, and cell division.
During mitosis, a single parent cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells, each containing a complete set of chromosomes. This ensures that the genetic information is accurately replicated and distributed, allowing for tissue growth and regeneration.
Meiosis: Cell Division for Reproduction
Meiosis, on the other hand, is a specialized form of cell division that occurs in germ cells—cells involved in sexual reproduction—and is essential for the production of gametes (sperm and egg cells). Unlike mitosis, which results in the formation of identical daughter cells, meiosis involves two successive divisions, known as meiosis I and meiosis II, resulting in the formation of four haploid daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
The process of meiosis is crucial for genetic diversity and variation, as it leads to the reshuffling and recombination of genetic material through processes such as crossing over and independent assortment. This ensures that offspring inherit a unique combination of genetic traits from their parents, contributing to species evolution and adaptation.
Key Differences Between Mitosis and Meiosis
While both mitosis and meiosis involve cell division, there are several key differences that distinguish the two processes:
Purpose: Mitosis is primarily for growth and repair of body tissues, while meiosis is for the production of gametes and sexual reproduction.
Number of Divisions: Mitosis involves one division, resulting in two daughter cells, whereas meiosis involves two divisions, resulting in four daughter cells.
Genetic Variation: Mitosis produces genetically identical daughter cells, while meiosis generates genetically diverse daughter cells due to processes like crossing over and independent assortment.
Homework Help: Navigating the Complexities of Cellular Biology
Understanding the nuances of mitosis and meiosis can be challenging, but with the assistance of homework help services, students can navigate the complexities of cellular biology with ease. Homework helpers offer personalized explanations, diagrams, and examples to clarify concepts and reinforce learning. Whether you're struggling with understanding the stages of mitosis or the significance of genetic recombination in meiosis, homework help services are invaluable resources for academic success.
Conclusion: Mastering Mitosis and Meiosis with Homework Help
In conclusion, mitosis and meiosis are fundamental processes that govern cell division in living organisms. While mitosis is essential for growth and repair, meiosis is crucial for sexual reproduction and genetic diversity. By understanding the differences between mitosis and meiosis and leveraging homework help assistance, students can strengthen their grasp of cellular biology and excel in their academic pursuits. With the guidance of homework helpers, unraveling the mysteries of mitosis and meiosis becomes an achievable goal, paving the way for a deeper understanding of the intricate workings of life.