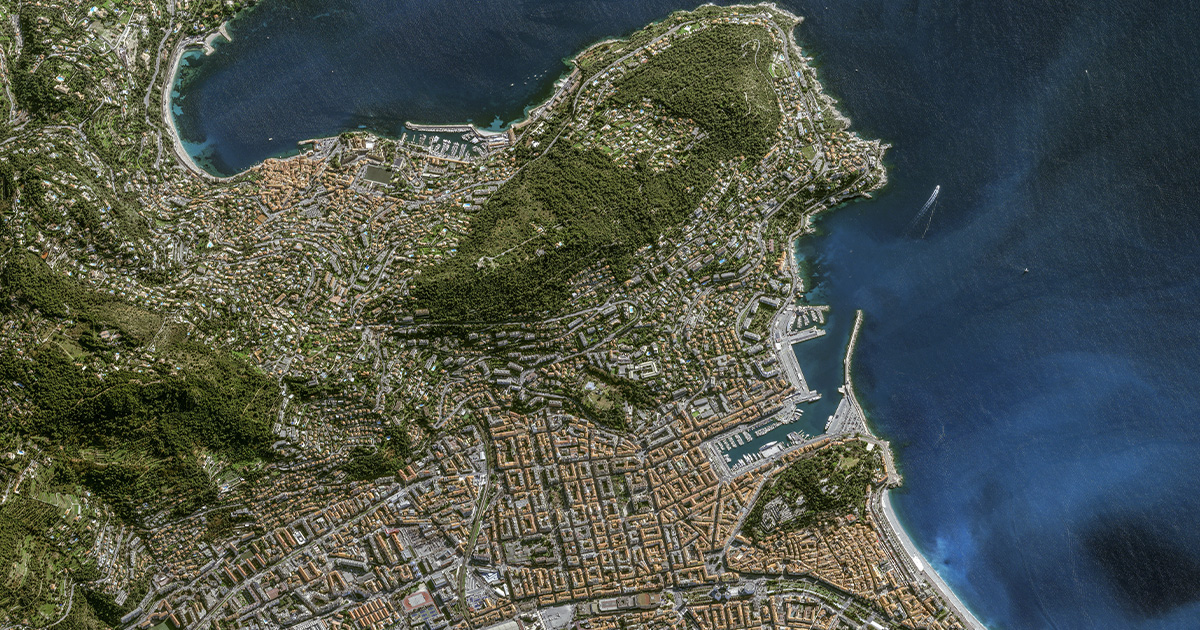
In the realm of geospatial technology, the Digital Terrain Model (DTM) emerges as a powerful tool, offering a three-dimensional representation of the Earth's surface. Beyond a mere digital elevation map, a DTM intricately captures the terrain's features, fostering a deeper understanding of landscapes. Join us as we embark on a journey through the fascinating world of Digital Terrain Models, exploring their applications, creation process, and the transformative impact they have on various industries.
The Essence of Digital Terrain Models: A Digital Terrain Model is a digital representation of the topography of a geographical area. Unlike its counterpart, the Digital Surface Model (DSM), which includes both natural features and built structures, a DTM focuses solely on the bare Earth's terrain. It acts as a visual blueprint, showcasing elevation changes, slopes, and landforms with remarkable precision.
Applications Across Industries: The versatility of Digital Terrain Models extends across a myriad of industries, revolutionizing the way professionals analyze and interpret geographical data. In urban planning, DTMs aid in understanding terrain variations for infrastructure development. In agriculture, they optimize land use planning by assessing slope gradients and water flow. Environmental studies benefit from DTMs by analyzing landscape changes, and in disaster management, these models assist in risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
Creating a Digital Terrain Model: The creation of a Digital Terrain Model is a meticulous process that combines cutting-edge technology and data acquisition methods. High-resolution satellite imagery, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) data, and aerial surveys contribute to the creation of detailed and accurate DTMs. Advanced algorithms and software then process this data, generating a comprehensive digital representation of the Earth's surface.
Precision and Accuracy: The success of a Digital Terrain Model lies in its precision and accuracy. The data sources used, such as LiDAR, provide elevation information with high resolution, ensuring that subtle terrain features are captured. This accuracy is crucial for industries where precise elevation information is paramount, such as in civil engineering projects or environmental modeling.
Visualizing Landscape Dynamics: DTMs offer more than static elevation data; they become dynamic tools for visualizing landscape changes over time. By integrating time-series data, professionals can analyze terrain evolution, monitor erosion patterns, and assess the impact of human activities on the landscape. This dynamic visualization capability enhances decision-making processes across diverse fields.
In the dynamic realm of Geographic Information Systems (GIS), Digital Elevation Models (DEM) take center stage, revolutionizing the way we analyze and interpret terrain data. A pivotal component of GIS, DEM serves as the key to unlocking a wealth of information about the Earth's surface. In this exploration, we delve into the intricate world of DEM in GIS applications, uncovering its significance, creation process, and the transformative impact it has on spatial analysis and decision-making.
Understanding DEM in GIS: A Digital Elevation Model in GIS is a digital representation of the Earth's topography, capturing elevation data across a specified area. By utilizing elevation values organized in a grid format, DEM provides a three-dimensional visualization of the terrain. This data-rich model becomes an invaluable asset in GIS applications, enabling professionals to analyze, model, and interpret landscapes with a heightened level of precision.
Applications Across GIS Industries: The integration of DEM in GIS significantly enhances spatial analysis across various industries. In urban planning, DEM facilitates slope analysis, aiding in the identification of suitable locations for infrastructure development. Hydrologists leverage DEM to model watersheds, analyze drainage patterns, and predict flood risk. In forestry, DEM helps assess terrain ruggedness for ecological studies. The applications extend to telecommunications, transportation planning, and natural resource management.
DEM Creation Process: Creating a Digital Elevation Model involves a meticulous process of data acquisition, processing, and representation. Technologies such as LiDAR, satellite imagery, and aerial surveys contribute to the collection of elevation data. GIS software processes this data, generating a grid of elevation values that forms the basis of the DEM. The accuracy of the DEM is contingent on the quality and resolution of the input data, making data acquisition methods a critical aspect of the creation process.
Spatial Analysis and Decision-Making: The precision of DEM elevates the spatial analysis capabilities within GIS. Professionals can conduct line-of-sight analysis, viewshed analysis, and slope analysis to inform decision-making processes. In environmental management, DEM aids in assessing terrain vulnerability to natural disasters. The ability to model and simulate terrain conditions empowers decision-makers with insights that contribute to sustainable development and risk mitigation.
Interoperability and Integration: DEM seamlessly integrates with various GIS datasets, enhancing the interoperability of spatial information. This integration allows professionals to combine elevation data with other layers such as land use, hydrology, and infrastructure, creating comprehensive geospatial models. The interoperability of DEM in GIS fosters a holistic approach to spatial analysis, enabling a more nuanced understanding of the relationships between different geographical features.
For More Info:-